python 三邊測量定位的實現(xiàn)代碼
定位原理很簡單,故不贅述,直接上源碼,內(nèi)附注釋。(如果對您的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,還請幫忙點個贊,謝謝了)
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-'''Created on Wed May 16 10:50:29 2018@author: dag'''import sympyimport numpy as npimport mathfrom matplotlib.pyplot import plotfrom matplotlib.pyplot import showimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib#解決無法顯示中文問題,fname是加載字體路徑,根據(jù)自身pc實際確定,具體請百度zhfont1 = matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(fname=’/System/Library/Fonts/Hiragino Sans GB W3.ttc’) #隨機產(chǎn)生3個參考節(jié)點坐標maxy = 1000maxx = 1000cx = maxx*np.random.rand(3)cy = maxy*np.random.rand(3)dot1 = plot(cx,cy,’k^’) #生成盲節(jié)點,以及其與參考節(jié)點歐式距離mtx = maxx*np.random.rand()mty = maxy*np.random.rand()plt.hold(’on’)dot2 = plot(mtx,mty,’go’)da = math.sqrt(np.square(mtx-cx[0])+np.square(mty-cy[0]))db = math.sqrt(np.square(mtx-cx[1])+np.square(mty-cy[1])) dc = math.sqrt(np.square(mtx-cx[2])+np.square(mty-cy[2])) #計算定位坐標 def triposition(xa,ya,da,xb,yb,db,xc,yc,dc): x,y = sympy.symbols(’x y’) f1 = 2*x*(xa-xc)+np.square(xc)-np.square(xa)+2*y*(ya-yc)+np.square(yc)-np.square(ya)-(np.square(dc)-np.square(da)) f2 = 2*x*(xb-xc)+np.square(xc)-np.square(xb)+2*y*(yb-yc)+np.square(yc)-np.square(yb)-(np.square(dc)-np.square(db)) result = sympy.solve([f1,f2],[x,y]) locx,locy = result[x],result[y] return [locx,locy] #解算得到定位節(jié)點坐標[locx,locy] = triposition(cx[0],cy[0],da,cx[1],cy[1],db,cx[2],cy[2],dc)plt.hold(’on’)dot3 = plot(locx,locy,’r*’) #顯示腳注x = [[locx,cx[0]],[locx,cx[1]],[locx,cx[2]]]y = [[locy,cy[0]],[locy,cy[1]],[locy,cy[2]]]for i in range(len(x)): plt.plot(x[i],y[i],linestyle = ’--’,color =’g’ )plt.title(’三邊測量法的定位’,fontproperties=zhfont1) plt.legend([’參考節(jié)點’,’盲節(jié)點’,’定位節(jié)點’], loc=’lower right’,prop=zhfont1)show() derror = math.sqrt(np.square(locx-mtx) + np.square(locy-mty)) print(derror)
輸出效果圖:
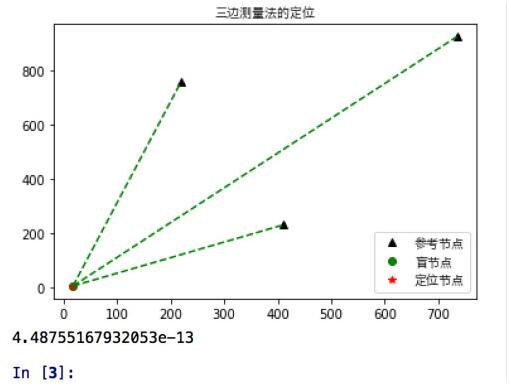
補充:python opencv實現(xiàn)三角測量(triangulation)
看代碼吧~import cv2import numpy as npimport scipy.io as scioif __name__ == ’__main__’: print('main function.') #驗證點 point = np.array([1.0 ,2.0, 3.0]) #獲取相機參數(shù) cams_data = scio.loadmat(’/data1/dy/SuperSMPL/data/AMAfMvS_Dataset/cameras_I_crane.mat’) Pmats = cams_data[’Pmats’] # Pmats(8, 3, 4) 投影矩陣 P1 = Pmats[0,::] P3 = Pmats[2,::] #通過投影矩陣將點從世界坐標投到像素坐標 pj1 = np.dot(P1, np.vstack([point.reshape(3,1),np.array([1])])) pj3 = np.dot(P3, np.vstack([point.reshape(3,1),np.array([1])])) point1 = pj1[:2,:]/pj1[2,:]#兩行一列,齊次坐標轉(zhuǎn)化 point3 = pj3[:2,:]/pj3[2,:] #利用投影矩陣以及對應(yīng)像素點,進行三角測量 points = cv2.triangulatePoints(P1,P3,point1,point3) #齊次坐標轉(zhuǎn)化并輸出 print(points[0:3,:]/points[3,:])
以上為個人經(jīng)驗,希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。如有錯誤或未考慮完全的地方,望不吝賜教。
相關(guān)文章:
1. 詳解Android studio 動態(tài)fragment的用法2. Android如何加載Base64編碼格式圖片3. 解決Android studio xml界面無法預(yù)覽問題4. 圖文詳解vue中proto文件的函數(shù)調(diào)用5. 什么是python的自省6. Spring Boot和Thymeleaf整合結(jié)合JPA實現(xiàn)分頁效果(實例代碼)7. Vuex localStorage的具體使用8. php模擬實現(xiàn)斗地主發(fā)牌9. vue 使用localstorage實現(xiàn)面包屑的操作10. Vue封裝一個TodoList的案例與瀏覽器本地緩存的應(yīng)用實現(xiàn)
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備